# should haves
library(tidyverse)
library(here)
library(lterdatasampler)
# would be nice to have
# performance allows us to check the performance of our models
library(performance)
library(broom)
# flextable allows us to make tables
library(flextable)
# ggeffects allows us to get predictions for models
library(ggeffects)
library(car)
library(naniar)Week 7 workshop
Week 7 Workshop
Izzy Tector
Linear Models
how does stem length predict stem dry mass
maples_data <- hbr_maples %>%
# & does the same as a comma would do in this case
filter(year == 2003 & watershed == "Reference")visualizing missing data
gg_miss_var(maples_data)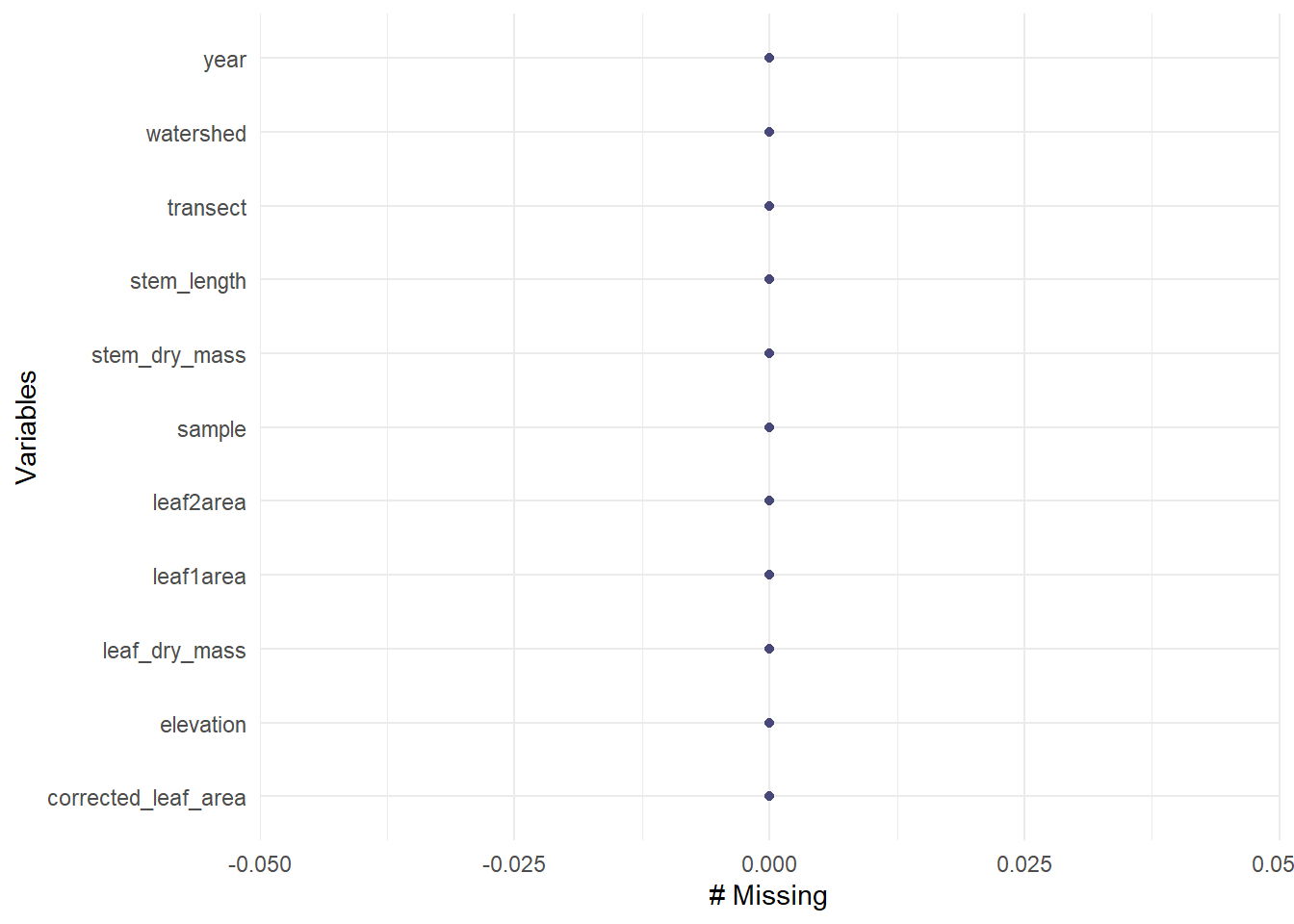
creating an exploratory data visualization
ggplot(data = maples_data, aes(x = stem_length, y = stem_dry_mass)) +
geom_point()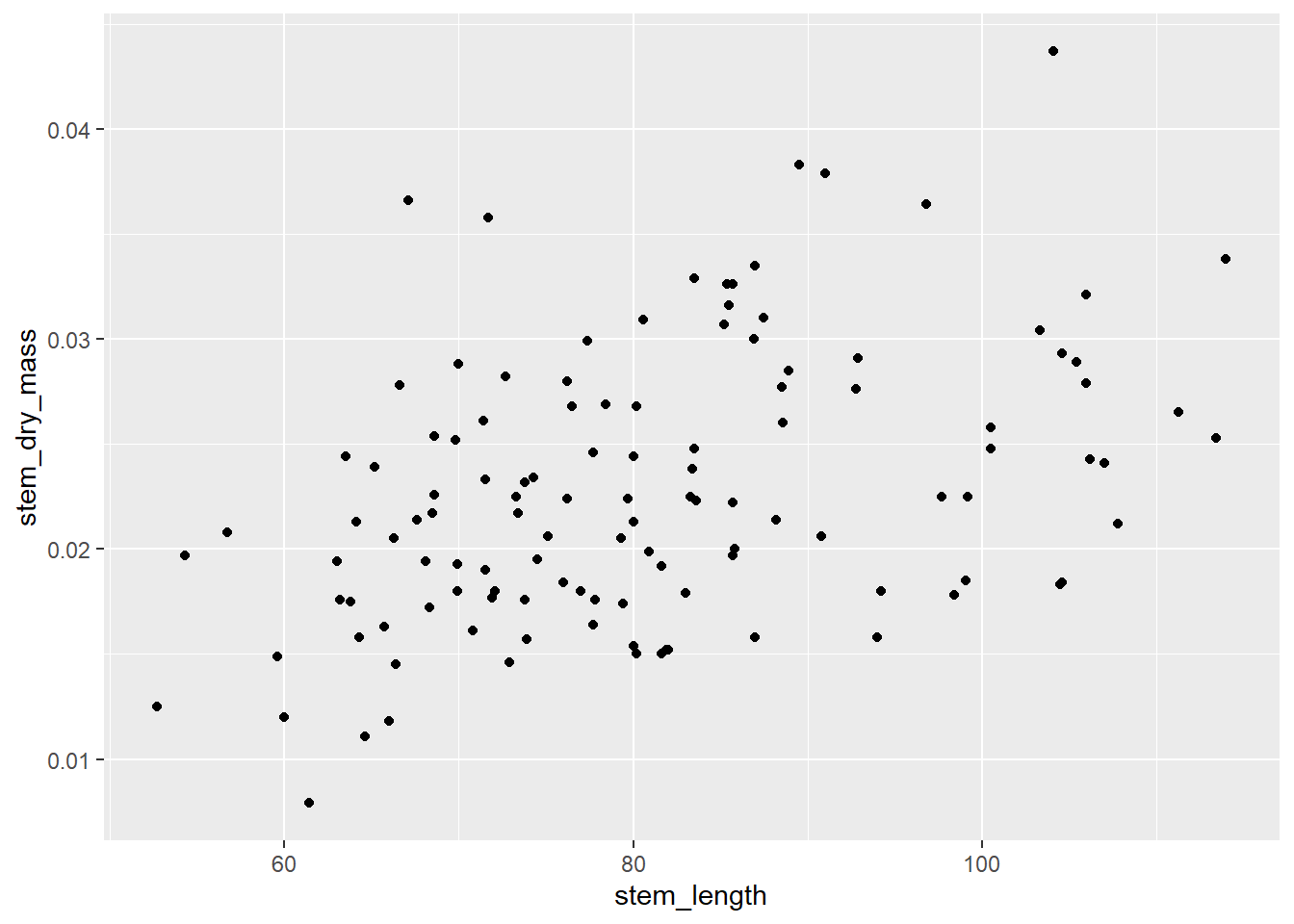
lets try a model
# we are going to be resuign this model a binch of times so it would be smart to make it an object
# lm makes a linear model
# for lm you put the y axis and what it is predicting after ~
maples_model <- lm(stem_dry_mass ~ stem_length, data = maples_data)
maples_model
Call:
lm(formula = stem_dry_mass ~ stem_length, data = maples_data)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) stem_length
0.0070033 0.0001958 check our assumptions
- linear relationship between variables: yes! (used the exploratory data visualization to check that)
- independence of errors: yes! (making that assumption based on how the data were collected)
- homoskedasticity: yes! (making that decision from residuals vs fitted plot/scale-location plots)
- normally distributed errors: yes! (looking at QQ plot of residuals)
# par allows us to set up a grid, preset in R, sets graphical parameters
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
plot(maples_model)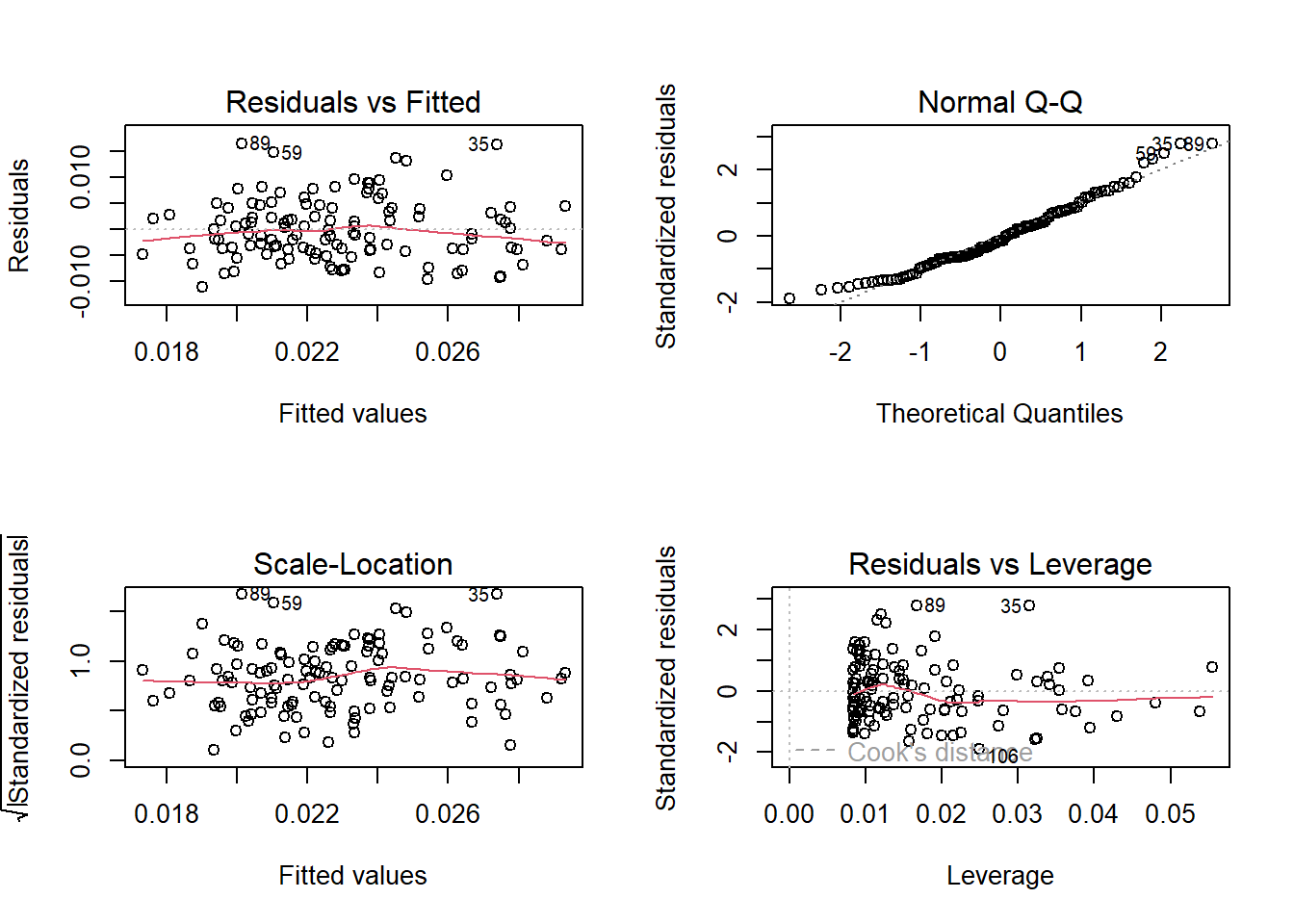
turn off the 2 by 2 grid
dev.off()null device
1